What is a financial asset?
An asset is a resource with economic value that owns or controls an individual or entity, which is interchangeable and from which it is expected to obtain future benefit. The issuance of an asset generates a debt to the issuing party (seller) and a right in the title (buyer).
For asset issuers, these represent a form of financing of their economic activity, since they receive money from the title buyer and generate the obligation of a future payment (generates a debt in the issuer). At the national accounting level, financial assets are not accounted for in the calculations of the Gross Domestic Product and, therefore, it is considered that they do not generate wealth in the country, although they contribute to economic growth by facilitating the movement of resources.
Types of financial assets
Among the most frequent types of financial assets we can find current money, bank deposits, loans, bonds, bills and shares of companies. In the classification of assets, different criteria can be used and different types can be described according to the criterion used.
Classification according to liquidity
- Legal currency
- Money in banks: bank deposits, checking accounts, savings accounts, etc.
- Promissory notes: promissory notes are issued by private companies.
- Public debt: short, medium and long term. The bonds and bills of the public treasury are financial assets issued by the government as a means of financing.
- Fixed income: it is similar to public debt but they are assets issued by private companies.
- Shares: the shares are equity financial assets issued by private companies whose dividends are affected, among other factors, by the social, economic and political environment.
According to the issuer
- Central Banks
- Public treasure
- Private banks and financial entities
- Private companies in sectors different from the banking and financial sector
Assets in financial markets
Financial markets can be classified as primary and secondary markets.
In the primary market is where financial assets are created and it is here where assets are exchanged directly between the issuer and the buyer.
In the secondary market, financial assets are sold and purchased without the intervention of the primary issuer. That is, in these markets financial assets that were previously created are exchanged. In the secondary market, asset owners can sell them to a third party as well as buy other existing assets. For example, in the stock market the assets are the shares of companies and in the Forex market the asset is the money itself (see what is Forex?).
Main characteristics of the assets
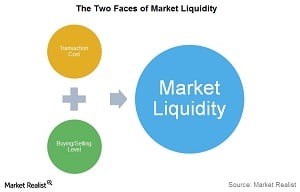
Financial assets are products intended for purchase and sale in financial markets and in this process three characteristics intervene: liquidity, profitability and risk.
- Liquidity:the liquidity of a financial asset can be defined as the ability to transform the asset into money in a short period of time, without affecting profitability and without this exchange leading to losses. In other words, liquidity would be the ability to sell quickly and effectively.
- Profitability: is the profit obtained when buying an asset. In general, the higher the return, the greater the risk associated with the asset. When there is a low risk the issuer offers a lower profitability; On the other hand, when there is a high risk, the issuer offers high profitability in order to find investors who accept the high risk.
- Risk: the risk associated with financial assets is the probability that the issuer of the asset is not able to comply with the obligations contracted with the buyer. For example, sovereign risk would be the risk associated with public debt securities. See also financial risk.