News about the expansion of the coronavirus makes headlines in the news. Many people wonder if this epidemic could spread on a large scale if it will be the next pandemic and will seriously affect not only a large part of the world’s population but also the global economy.
On Tuesday, February 4, the director of global preparedness for the risks of infection of the World Health Organization (WHO) explained that we still cannot talk about a pandemic (which would be when a disease spreads worldwide), but of an epidemic with multiple foci.
In addition to health effects, the impact on the global economy could be very high. If we move to the past only a few years ago we find SARS, the severe acute respiratory syndrome that had its origin in Southeast Asia, and that has some kinship with the coronavirus.
What is the relationship between SARS and the current coronavirus?
Coronavirus is a generic term that refers to a certain type of virus that shows a crown around it when examined under a microscope. The coronavirus that today has a part of the population in suspense has been baptized as 2019-nCoV. In December 2019 it was first detected in Wuhan, capital of the Chinese province of Hubei.

For its part, SARS was also caused by a type of coronavirus, which, according to WHO data, caused the death of 774 people out of 8,098 listed as infected.
In the summer of 2012, a group of scientists began a study to find the origin of SARS in a cave in the Chinese province of Yunnan, as a similar virus had been detected in a population of bats. The study lasted five years and concluded that the virus could have been communicated from bats to civets (small mammals that are consumed by humans in some regions of Asia) and from there to people. In addition, the scientists explained that there were more types of coronaviruses, so it was possible that in the future there would be more similar epidemics.
Now, the epicenter of this crisis is in Wuhan. Although it is almost two thousand kilometers from where the SARS study was conducted, the origin seems to be the same: a market in which different animal species were stacked for sale for consumption: bats, civets, badgers, and other species.
What are the prevention measures?
Although the origin of the disease is, in principle, animal, infection between people is possible. Coronavirus is transmitted through the air and through physical contact, similar to the flu. Therefore, in the same way that happens with flu, it is important to avoid physical contact with people who may be infected, frequently wash their hands with soap and water and avoid touching their eyes and nose.
For their part, the authorities of Hubei Province have also taken other measures, such as the distribution of millions of masks and tens of thousands of packages of protective medical clothing. In addition, there are about fifty million people in a quarantine situation, as the authorities do not allow them to leave the area where the epicenter of the disease is located, as a precautionary measure imposed by the Chinese authorities.
What is the current situation of the epidemic?
It should be remembered that, at the beginning of February, the disease is centered mainly in Southeast Asia, mainly in China, where there are more than 20,000 registered cases and more than 426 people have died from this virus.
Other countries in the area have some incidence, but much smaller: 25 affected in Thailand, 20 cases in Japan, 18 in Singapore, 16 in Korea, 10 in Taiwan and Malaysia or 2 in the Philippines, where the only person outside has died from China.
Meanwhile, in Europe cases are counted, with 12 affected in Germany, 6 in France, 2 in the United Kingdom and in Italy, or 1 in Spain, which is located in the Hospital of La Gomera.
In other areas of the world, there are also some affected, such as in the United States (11 cases), in Canada (4) or in Australia (12).
In China, the epicenter of the disease, the authorities have built a gigantic hospital using prefabricated modules in just ten days, with a capacity of 1,000 beds and about 1,400 employees, to serve the affected population and keep it in quarantine. In addition, another hospital with capacity for another 1,500 beds is already being prepared.
On the other hand, to counteract the negative effects already suffered by its stock market and which has an impact on the economy in general, the Chinese government has announced a gigantic monetary injection of some 160,000 million euros.
All this, on the basis that the Chinese economy already suffered a slowdown, so that its “meager” current growth of 6.1% could be reduced to 5% or even less, in the first estimates.
How can a pandemic affect the global economy?
At the moment, as we indicated at the beginning, the coronavirus 2019-nCoV has not reached the category of pandemic, since it has not spread on a large scale globally. However, its effect on the economy may already be high, being focused on one of the global economic giants.
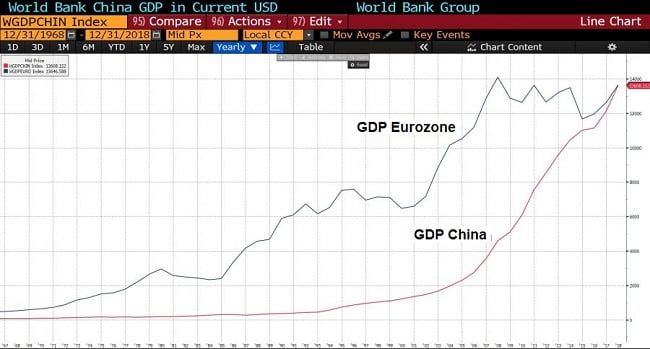
According to a study by the University of Korea, the global impact on the economy produced by SARS was about $40 billion. Today, the effect of a crisis like this could be even greater, because the Chinese economy is more important and, in addition, there is greater globalization. In the SARS crisis, the weight of the Chinese economy in the world GDP did not exceed 5%, while currently, this figure has risen to 16% today.
Some estimates indicate that the effect on the Chinese economy could be between 1% and 1.5%, with which we would be talking about an impact of between 120,000 and 180,000 million dollars.
Which can be the most affected sectors?

Tourism – and related sectors such as airlines or airport managers – is one of the areas that may be most affected. And it happens both ways: millions of people will stop traveling to that area of the world, while other areas will stop receiving Chinese tourists, in many cases with high purchasing power.
The energy sector is another that could be affected, since it must be remembered that China is the second largest consumer of oil worldwide, behind the United States, and the largest consumer of coal (an estimated 70% of the country’s energy is produced through this commodity).
Jewelry, watches and other products related to luxury and fashion are also affected by this crisis. And, although the Asian giant is still an economy in which an important part of its population lives on low incomes, the number of rich people there grows exponentially.
In fact, in 2019 China surpassed the United States as the country with the most millionaire people, according to a report published by Credit Suisse. There are more than 100 million Chinese, with savings of more than $109,430 (a figure that marks the border of 10% of the richest population), while there are “only” 99 million Americans in that situation.
In addition, any sector that manufactures in China – the vast majority – can be affected by quarantine measures and the general break of the Asian giant. As an example, it has been announced that the launch of Apple’s new model, the new iPhone, could be delayed. Although the forecast was to present the new phone this February, two of its main suppliers, Foxconn and Pegatron have their factories in places relatively close to Wuhan.
Recent epidemic and endemic diseases
In recent years there have been other major epidemics. One of the most serious has been that of Ebola, which caused more than 11,000 deaths. The epidemic was centered mainly in the African continent, in three countries: Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea.
Another disease such as cholera, although today it is easy to prevent and treat, in certain circumstances, it is still capable of causing epidemics. This is the case in Yemen, due to the destruction of the sanitation infrastructure caused by the successive wars.
Endemic diseases are those that settle over time in an area and affect a population group. The main example is malaria, in some African countries.
It could also be included in this category a virus that had a high incidence in Europe but is currently controlled: HIV, which causes Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). However, in some countries in sub-Saharan Africa, it has been installed as a chronic disease that continues to kill tens of thousands of people every year. In several of these countries (Bostwana, Namibia, or Zimbabwe), more than 10% of the adult population has HIV.